Basic Sewing Terms – an Illustrated Dictionary
Are you ready to join the ever-growing group of enthusiasts around the world who enjoy sewing as a hobby and to even turn it into a profession?
Here is a brief introduction of the ABC of sewing, including all basic terms and definitions which you need to learn about this useful and enjoyable craft. It will require some time a patience, as well as experience so that you get familiar with these terms and learn how to use them and perform them properly and with ease, but believe me, once you get the hang of it – it becomes quite simple and straightforward.
Let’s get started with all the basic terms you will need in order to become an experienced sewist:
Glossary of sewing terms
Anchoring stitches
Machine sewn stitches with zero length for the end of the seam – made to prevent it from pulling out.
Applique
This is the action of sewing a piece of fabric on top of another with a tight zig-zag stitch.
Asymmetrical bias garment
A bias cut garment which is not an exact mirror image of itself from one side to the other.
Back-stitch
As the name suggests, this is the action of sewing backwards by holding the reverse button or lever on your sewing machine. This is done when you need to knot the cloth you are working on.
Baste
This is the longest possible stitch you can do with your sewing machine or one which you will do by hand when beginning a sewing project. It is long and loose and has no knots either at the beginning or the end. To baste you have to set the stitch length at the longest possible setting on your sewing machine. The baste is used for holding the fabric together before proceeding with the actual sewing.
Basting needle
A long hand-sewing needle used for basting.
Bead elastic
Strong cord which is stretchable and is used for jewelry making and beading.
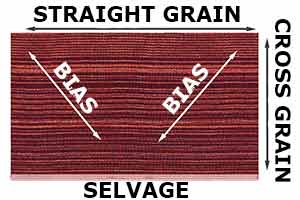
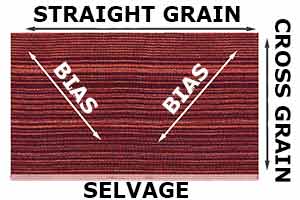
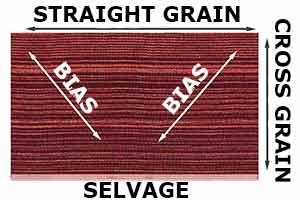
Bias
This is the 45 degree angle from the fabric grain. If you turn the fabric diagonally (at 45 degrees) and cut it from the bottom of the fabric, you will be cutting at the bias. This is done when a certain pattern needs to be met or followed in order to make a dress, skirt or other garment hang properly.
Bias tape
You can make it yourself or purchase a bias tape. It is used to edge corners and fabric items.
Blanket stitch
Hand sewn stitch used for finishing the edges, similar to a buttonhole stitch.
Bobbin
The thread which comes from the bottom part of the sewing machine to meet your spool thread at the needle and form the stitches. Bobbins need to be winded and then inserted into the machine, which requires some practice and learning.
Bodice
The upper part of the apparel from the shoulders and neck to the waist.
Boning
Narrow strips made of plastic, bone or metal used for stiffening the garment at certain areas.
Buckram
A coarse and heavy garment used to stiffen various garments as well as hats.
Buttonhole
This one is pretty obvious – it is the hole which you need to sew for the button to be pulled through. The majority of the sewing machines can sew buttonholes automatically, but if you need to do it by yourself, just sew two parallel satin stitches at the length of the button and then slice open the middle to create the actual hole. Remember to sew them so that the two stitches at both ends remain connected.
Catchstitch
A type of hem stitch which is used to join an edge on the inside of the clothing and is formed with cross-shaped stitches on one of the sides of the edge.
Constant reference point
A point on the fabric which never changes used for reference and measurements.
Compass rule
The use of a pinned string or other marking device to create a circle by using it as a radius.
Couture
The high end clothing made by leading designers in the fashion industry which are custom fitted and hand sewn.
Crochet
A method used for creating a garment, lace, fabric or braid with the help of a hooked needle and yarn.
Cross grain
The part of the grain which is perpendicular to the selvage.
Dart
Used around waist, hip, bust lines and shoulder areas to give a shape to the fabric for these curved areas.
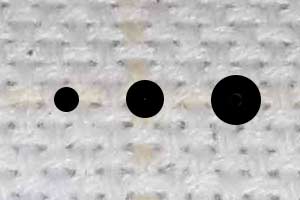
Dots
They vary in size and are used for marking the fabric indicating starting or stopping points for the stitching, or for other marks you will be needing and using while working on your project.
Double needle
A pair of sewing machine needles which are placed and used simultaneously to create a set of two parallel rows of stitches at the same time.
Drape
The fluid way in which the fabric of a garment hangs.
Ease
The difference between the body measurements and the measurements of the garment which allows for sufficient space for the body to move freely.
Embroidery
The hand or machine sewing technique which is used to create decorations on a fabric. The threads can be colorful and can be also embroidered with the help of programmable sewing machines.
Fabric
The main material you will be using for your sewing projects, this is possible the first element of your project which you will pick. Learning to tell the difference between weft and warp and finding the grain and using the muslin is an essential skill you will need to learn when starting up sewing as a hobby or profession.
Facing
Partial lining which is used for certain areas, such as necklines or arm holes to give the garment a nicely finished edge without the use of a full lining.
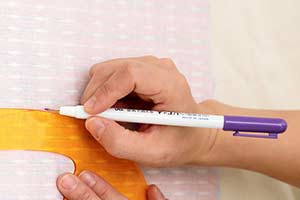
Fading pen
A special pen which you can use to make markings on your fabric and which will disappear after 12-24 hours after you have used it.
Fat quarter
This is a cutting technique which involves cutting a whole piece of fabric in the middle horizontally and vertically (like a plus sign) which leaves four pieces of fabric at the end. Each of the pieces is called a fat quarter.
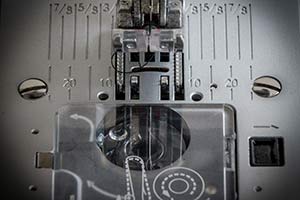
Feed dog
A toothed metal unit under the stitch plate which moves down and up to push the fabric along while you are sewing.
Foot pedal
This is the pedal of the sewing machine which you press with your foot in order to make the machine’s needle sew. Where you place the pedal and which foot you use is up to you.
Fusing
Also known as “heat’n’bond” is the item you use to stick one piece of fabric to another by placing it between the two pieces, peeling the paper back off it and ironing it, so that it sticks.
Gather
You gather the fabric in order to create ruffles on your garment. Baste stitch it, hold the threads at both ends and pull them gently so that the fabric gets ruffled. Remember to keep the bottom thread steady for a proper effect. Once you create the gather you want, sew it properly so that it stays that way permanently.
Photo by Love to Sew Studio / CC BY / Cropped from original
Godet
A triangular piece of cloth used for adding fullness and added in the hem of a skirt.
Photo by Sophus Bie / CC BY / Cropped from original
Grain
The threads which go up and down and sideways in your fabric in a perpendicular manner.
Grainline
A long and narrow arrow symbol which is printed on the pattern and which corresponds to the grainline of the fabric.
Hand
The term which is used for describing the feeling and texture of the fabric.
Hand wheel
The hand wheel of your sewing machine which you will use to adjust the height of your needle.
Hem
The edge which you need to sew at the bottom of a garment. To hem, fold the bottom of the fabric by half an inch and fold it once again and stitch it properly in place.
Hemline
The lowest part of a dress or garment once the hem is already sewn.
Inseam
The vertical seam sewn in between the legs of pants.
Interfacing
Used for stabilizing the fabric or making it more study, the interfacing can be of the type which is ironed to the fabric, or needs to be sewn on to it.
Photo by kellyhogaboom / CC BY / Cropped from original
Knot
Knotting is done by sewing forward and reversing on top of it by about an inch, and then sewing it forward again. It will ensure that the stitch doesn’t get undone.
Ladder stitch
A stitch used to join two folded edges of fabric. The stitches are tight and done at right angles to the fabric, and crate a ladder like shape and formation between the pieces. These are tightened and are invisible.
Lapel
The piece of the garment where it connects with the collar.
Lining
This is the fabric layer which goes beneath your main fabric. Usually the lining is of neutral color and is used to add more substance to a garment or make it less see through.
Photo by kellyhogaboom / CC BY / Cropped from original
Machine tension
It is controlled by disks and adjusts the drag applied to the thread depending on the type of fabric and thread used.
Milliner’s needle
A long needle which is very thin and doesn’t get wider towards the eye, originally made for hat making.
Muslin
A cotton fabric which is undyed and untreated and is used to create different pattern pieces as well as prototypes in the garments, so that you can check the design and fix any mistakes before using the real fabric.
Nap
Fuzzy fabrics like velvet, fleece and others. Certain fabrics have one direction naps which means that you need to be extra careful when sewing the different pieces of your project together, so that the direction of the nap is the same throughout.
Notches
Used to line up several pieces of fabric together and keep them aligned properly and in a straight manner, so that you can sew them or otherwise adhere them together in accordance to your design.
Photo by crystalflickr / CC BY / Cropped from original
Notions
The sewing accessories which you will use for your sewing project, such as: buttons, zippers, bias tape, pins, thread and others.
Ombre
Closely related hues of the same color which graduate from lighter to darker.
Outline
The cutting line of a pattern which is its outline.
Pattern drafting
To draw a design on paper before proceeding to do it with fabric.
Pins
These you will be using a lot. They are used to keep the different pieces of fabric in place before proceeding to sew them. The pins should be placed in a way which allows the needle to stitch through them without hitting on the pin heads or so that you are able to easy slide them off as you are sewing your garment.
Pin cushion
This is used for easy accessibility to your pins.
Piping
Narrow, bias cut fabric which is folded over a cord and can be inserted in the seam of a piece of clothing in between the facing and the edge as a decorative item.
Photo by jennerosity / CC BY / Cropped from original
Placket
Overlapping fabric which covers the openings in a garment and can hide or support these closures.
Pleat
A fold on the fabric created by doubling it over and then stitching it together.
Pocket patch
A pocket sewn on the garment’s face side.
Preshrink
Washing the fabric before cutting or sewing it.
Press
To iron a fabric.
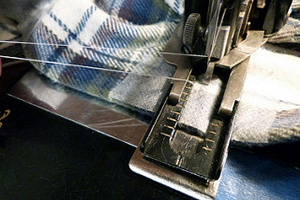
Presser foot
The little metal piece near the needle on the sewing machine which is lowered in order to press down the fabric so that it can be stitched properly and evenly and to keep it in place.
Quilting
The stitching of two layers of fabric together, with added filling and following a consistent pattern.
Raglan sleeve
A design of the sleeve where the sleeve and shoulder are in cut in one or two pieces.
Raw edge
The fabric edge which is cut.
Right side
Most fabrics have a right side, which is the side with the patterns, colors and designs.
Right sides together
This is the action of placing two pieces of fabric together in a way which allows the right sides to touch each other.
Rise
The distance between the crotch and the waist band on pants.
Roving
Clean fiber which has not been spun.
Ruche
A strip of fabric which is gathered or pleated.
Seam
The line where the fabric is sewn to another piece of cloth for your project.
Seam allowance
The amount of fabric which you leave between the edge and your stitch.
Seam guides
These are built into the sewing machine to help you set and keep the correct seam allowance while sewing the seams of your garment.
Seam ripper
A sharp tool used for ripping out a seam which you have sewn wrong.
Seam tape
A ribbon like, stable and light tape which is used for stabilizing hems and seams.
Selvage
This is the finished edge of the fabric when you first purchase it.
Serger
A sewing machine which can trim, seam and overcast the raw edges of a fabric in one step. Also known as: overclock machine.
Sewing machine needles
The needles which you use for your sewing machine. They come in different varieties, and you should have extra ones handy in case your needle breaks while working on your project.
Sewing scissors
Very sharp scissors which allow you to cut the fabric properly. These should be used for cutting fabric only in order to keep them sharp and precise.
Shoulder point
The position of the seam at the shoulder where the arm and the shoulder connect.
Singe crochet
The most basic stitch used for crocheting.
Single layer layout
A pattern layout for a single layer of fabric, used for garments which are asymmetrical and have unusual patterns, shapes and sizes.
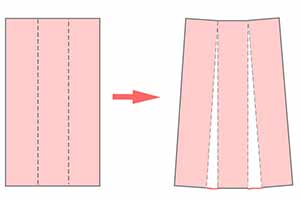
Slash and spread
Cutting a pattern and spreading it along the cutline for added fullness to a certain section.
Slashed pocket
A pocket which is cut through the garment face and is faced.
Sleeve cap
The part of the sleeve which is above the biceps line.
Sloper
A master pattern which is used to create perfectly fitting snug basic garments, and is used to fit commercial patterns.
Spool of thread
The thread on the top of the machine which is used for the top of the stitches you make (the bottom thread comes from the bobbin). You need to learn how to thread your spool on your machine. Threads come in a wide variety of types and colors.
Spool pin
The part of your sewing machine where you place the spool and from which the thread is fed to the needle.
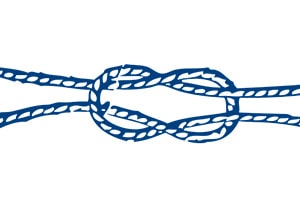
Square knot
A knot which forms a square, commonly known as macrame.
Stabilizer
An under layer fabric which is used for holding the shape and support the fabric.
Photo by kellyhogaboom / CC BY / Cropped from original
Stitch length
The length of a stitch which is determined by the feed dogs of the sewing machine.
Straight grain
The part of the grain which is parallel to the selvage.
Straight stitch
The most basic type of stitch made with a sewing machine – single stitches in a straight row.
Tambour needle
Sharp and thin hook which is used for applying sequins or strung beans or sewing decorative stitches on the fabric.
Tapestry needle
A needle which has an oval shaped eye and a blunt tip and is used for decorative stitching with yarns and other bulky threads.
Thread cutter
Used to cut the end of the thread, some of the best starter sewing machine models have it built in.
Thread trace
Transferring the markings from the pattern to the fabric with the help of basting stitches in order to duplicate the pattern markings.
Top stitch
A stitch which you will make as a finishing touch on top of a seam which you have sewn already.
Tricot
A thin, nylon fabric which is commonly used for underwear.
Tulle
Fine netting which is used for veils, gowns and others.
Turn
The action of turning the sewn fabric with the rights side in.
Underlap
The lower layer of fabric of two overlapping pieces of fabric on a garment.
Underlay
A fabric layer underneath another fabric layer.
Understitch
When seam allowances are stitched along an edge to the facing.
Waist stay
A stable ribbon which is sewn inside the waist of a dress to support it.
Warp
The thread which runs through the length of a woven fabric – up and down.
Weft
The cross grain – threads which run at right angles through the length of a woven fabric.
Webbing
This is a braided strip of fabric resembling a belt which can be used for making straps for a bag or other.
Whiskers
The frayed, tiny threads on the raw seam edges of the fabric.
Wrong side
This is the underside of the material you are using – the other side of the right side. There are some types of fabric where both sides are the same, but in many cases, the fabric has a right and a wrong side.
Yardage
The term used in the US for the cut length of fabric. Fabric is measured in yards (intervals of 36 inches).
Yoke
The design element on top of the garment which is made to fit over the body.
Zigzag
A stitch with a zigzag pattern, which is usually used along the edges of the apparel to keep them from fraying, or for an applique or satin stitch.
Zipper
Zippers are used for a multitude of garments and other sewing projects. There is a huge variety of zipper types, shapes, colors and sizes, so make sure you know what you will be needing when going to the store to pick one.
Zipper coil
A nylon filament which forms the teeth in a zipper.
Zipper foot
A special presser foot which allows for easy and precise sewing of the zipper with a needle close to the zipper teeth.
Zipper guard
The double layered fabric which is sewn behind the teeth of the zipper to keep the skin protected from the zipper teeth, and from getting pinched or otherwise hurt when opening or closing the zipper.